B7-H7/HHLA2
EXCITING NEW TARGET
Immunotherapies targeting the B7 receptor family such as PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 have improved outcomes for many patients and have revolutionized oncology treatment over the past two decades. B7-H7, also know as HHLA2, is a B7 family member whose inhibitory receptor, KIR3DL3, has been recently identified by our co-founders.
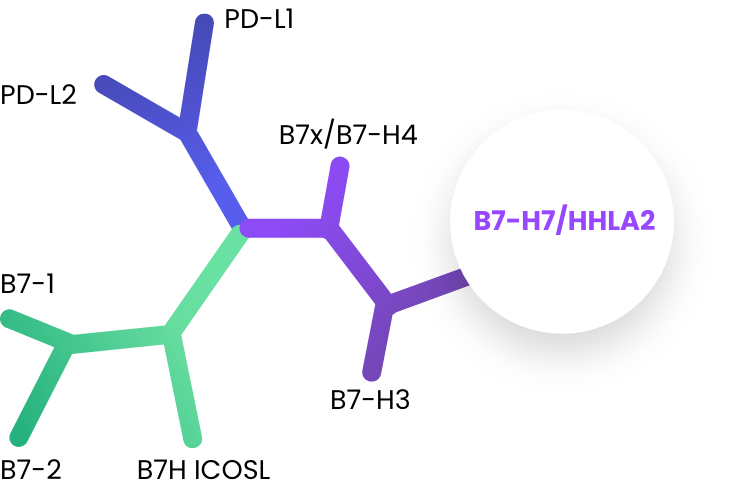
A Novel Immuno-Oncology Checkpoint
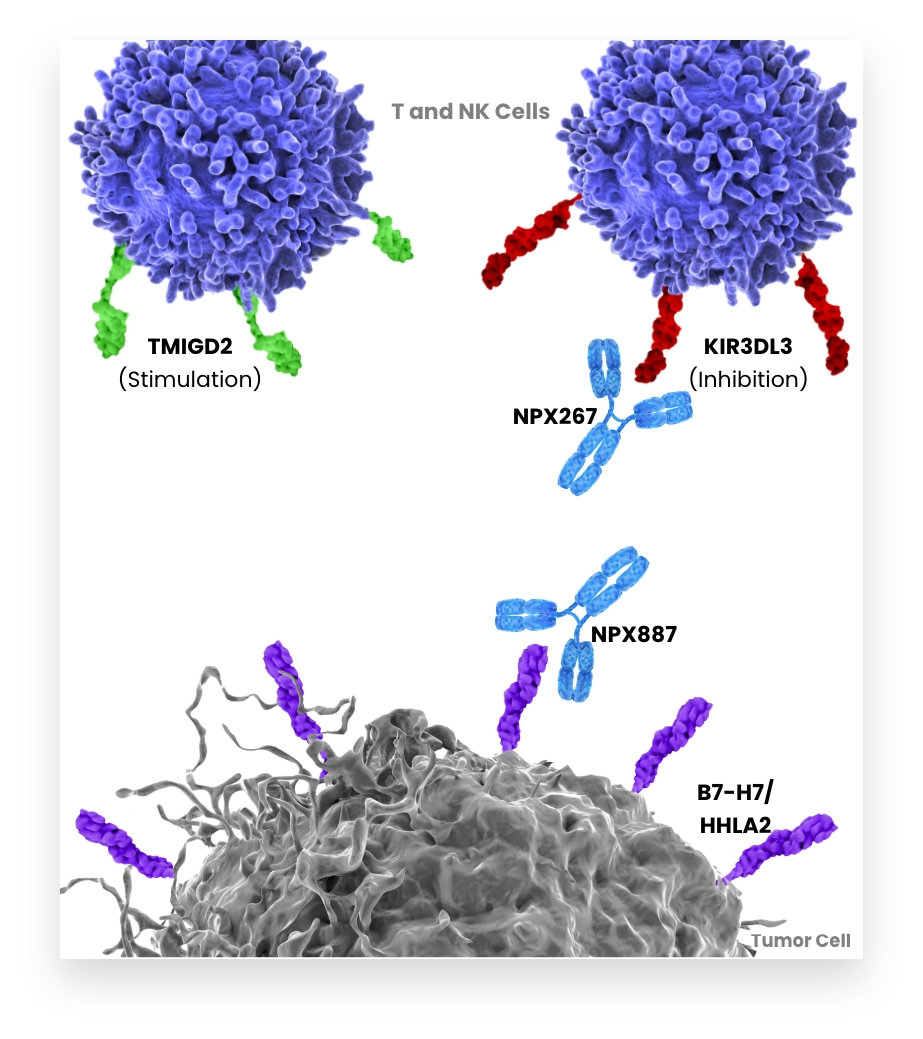
B7-H7 inhibits activation of T and NK cells via KIR3DL3. Tumors expressing B7-H7 suppress T and NK cells within the tumor. Therefore, blocking B7-H7-KIR3DL3 interaction to enhance the anti-tumor immune response is an attractive strategy for cancer treatment. B7-H7 has also been shown to bind an activating receptor TMIGD2. To explore the full potential of this axis inhibition, NextPoint Therapeutics is pursuing both B7-H7 and KIR3DL3 specific antibodies, is generating multiple approaches to enable tumor targeting and is approaching modulation of TMIGD2-mediated activity.

A New Tumor-Associated Antigen for Tumor-Targeting Therapies
Strong overexpression of B7-H7 in tumor tissues with limited expression in normal tissues makes it an attractive target for tumor targeting approaches, which can be directed to the tumor via antibody-based binding to B7-H7. These include: targeted chemotherapies (antibody-drug conjugates), targeted radiotherapies, and T cell engagers.
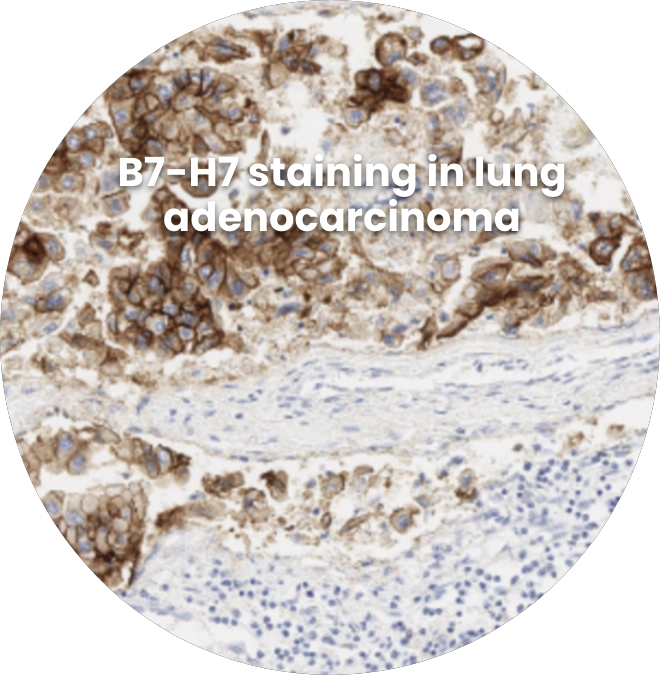
A Potential Biomarker to Identify Patients Most Likely to Respond
NPX267
Designed to reverse T and NK cell Suppression
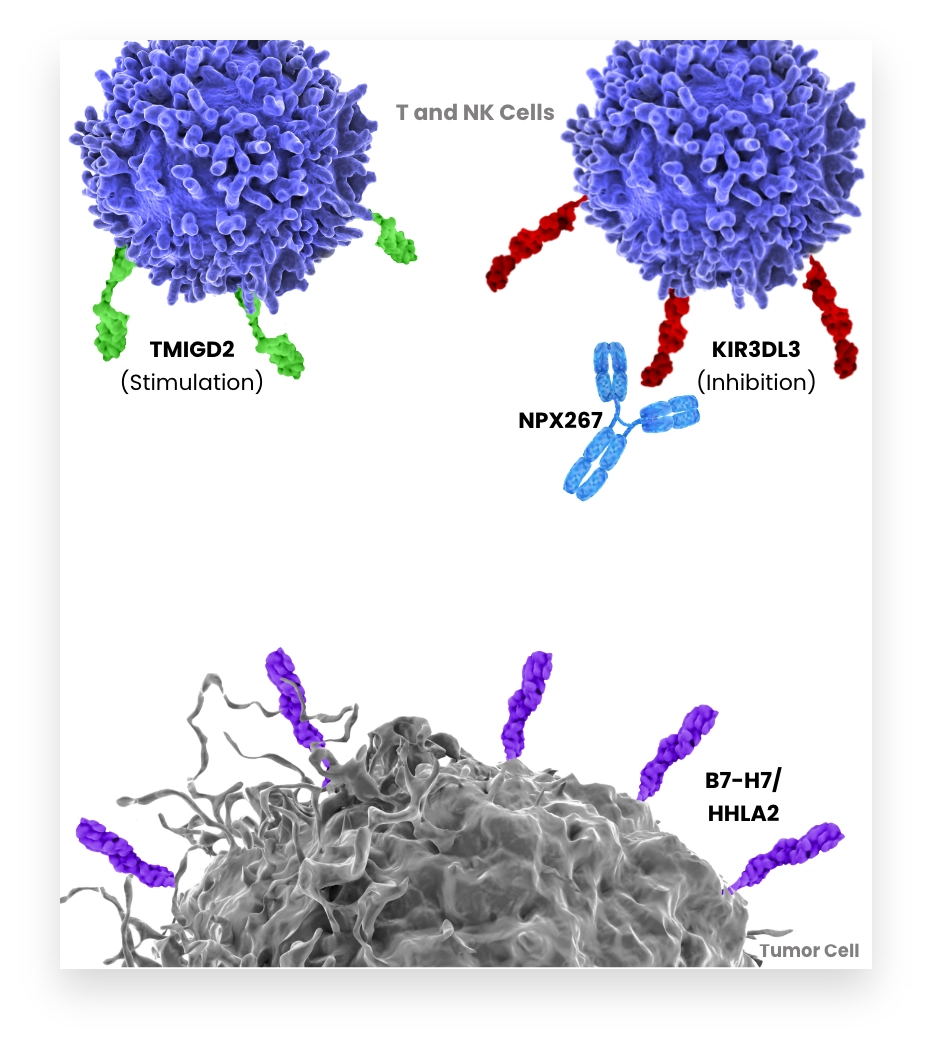
Our co-founders independently identified KIR3DL3 as the inhibitory receptor for B7-H7.
KIR3DL3 binding to B7-H7 interferes with the anti-tumor potential of T and NK cells and can contribute to tumor immune escape.
KIR3DL3 is unregulated on a subset of antigen-experienced, exhausted effector memory T cells, called TEMRA cells, and on a subpopulation of NK cells.
NPX267 is being studied in a phase 1 clinical trial in solid tumor malignancies known to express B7-H7.

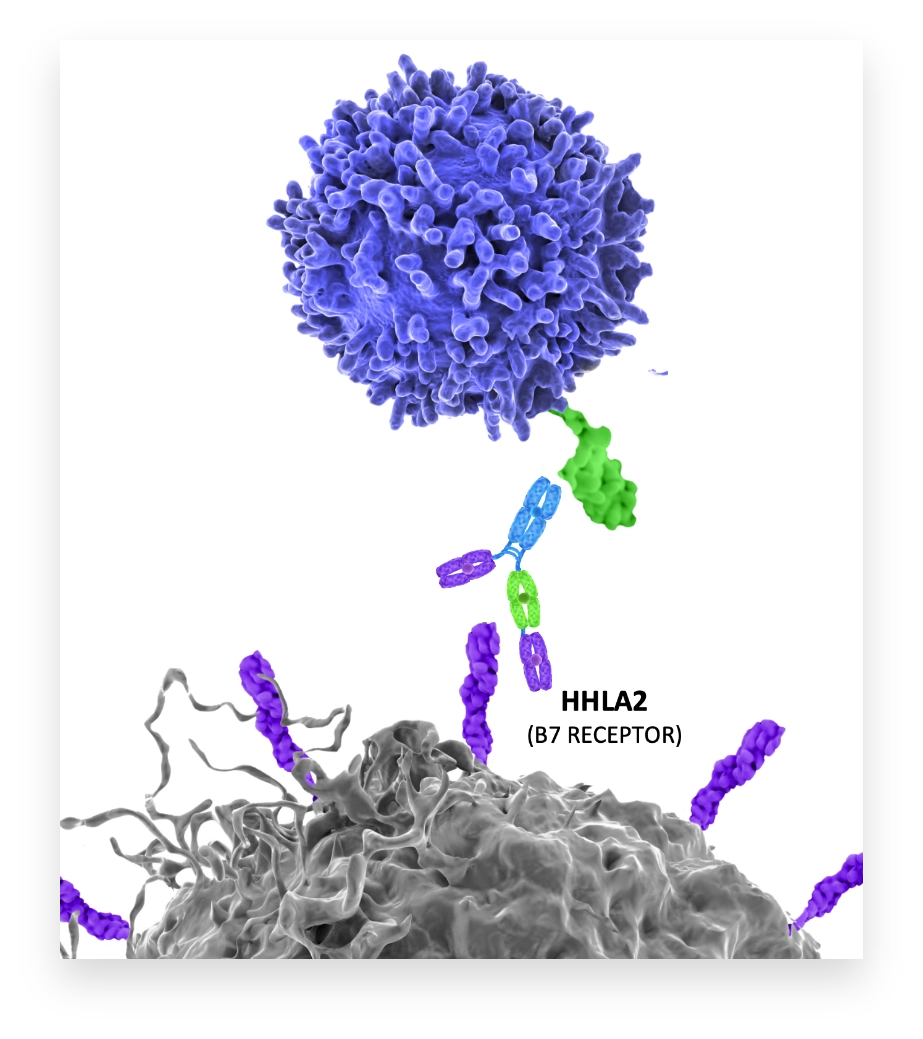
NPX887
Designed to block immunosuppression by KIR3DL3 while sparing immunostimulation by TMIGD2

NPX887 targets B7-H7 to block its interaction with KIR3DL3 and to prevent immunosuppression of T and NK cells.
NPX887 enables the interaction of B7-H7 with its other ligand, TMIGD2, which can stimulate T and NK cell activation.
NPX887 has enhanced Fc receptor function to potentiate ADCC- mediated destruction of B7-H7-positive tumor cells.
NPX887 is being studied in patients with solid tumor malignancies known to express B7-H7 in a phase 1 clinical trial.
NPX372
Designed to……CONTENT GOES HERE……CONTENT GOES HERE

Strong overexpression of B7-H7 in tumor tissues with limited expression in normal tissues makes it an attractive target for tumor targeting via T cell engager.
NPX372 is an IgG-like T cell engager with two B7-H7 binding domains, a single CD3 binding domain, and an inactivated Fc. Both B7-H7 and CD3 binding domains are cross-reactive to NHP and human targets.
NPX372 mediates potent in vitro tumor cytotoxicity with B7-H7 expression level dependency. NPX372 demonstrates efficacy across several in vivo models with complete tumor regressions.
NPX 372 can be safely administered preclinically up to mg/kg dose levels. IND submission is planned for 2025.

