THE SCIENCE
Our Approach
EXCITING NEW TARGET
B7-H7/HHLA2 is an Exciting New Target
Immunotherapies targeting the B7 receptor family such as PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 have improved outcomes for many patients and have revolutionized oncology treatment over the past two decades. B7-H7, also know as HHLA2, is a B7 family member whose inhibitory receptor, KIR3DL3, has been recently identified by our co-founders.
- B7-H7 is expressed independently of PD-L1 and acts through 1) a unique inhibitory receptor, KIR3DL3 to block T/NK cell activation and 2) a unique stimulatory receptor, TMIGD2, to increase T and NK cell activation.
- The upregulation of B7-H7 expression in tumor tissues makes it an ideal tumor-targeting antigen for many different therapeutic payloads in oncology.
- The selective expression of B7-H7 in tumor cells enables a biomarker strategy to select patients most likely to benefit from these targeted therapeutic approaches.
STRATEGY
B7-H7/HHLA2 - A Novel Immuno-Oncology Checkpoint
STRATEGY
B7-H7/HHLA2 - A Novel Tumor-Associated Antigen for Tumor-Targeting Therapies
Strong overexpression of B7-H7 in tumor tissues with limited expression in normal tissues makes it an attractive target for tumor targeting approaches, which can be directed to the tumor via antibody-based binding to B7-H7. These include: targeted chemotherapies (antibody-drug conjugates), targeted radiotherapies, and T cell engagers.
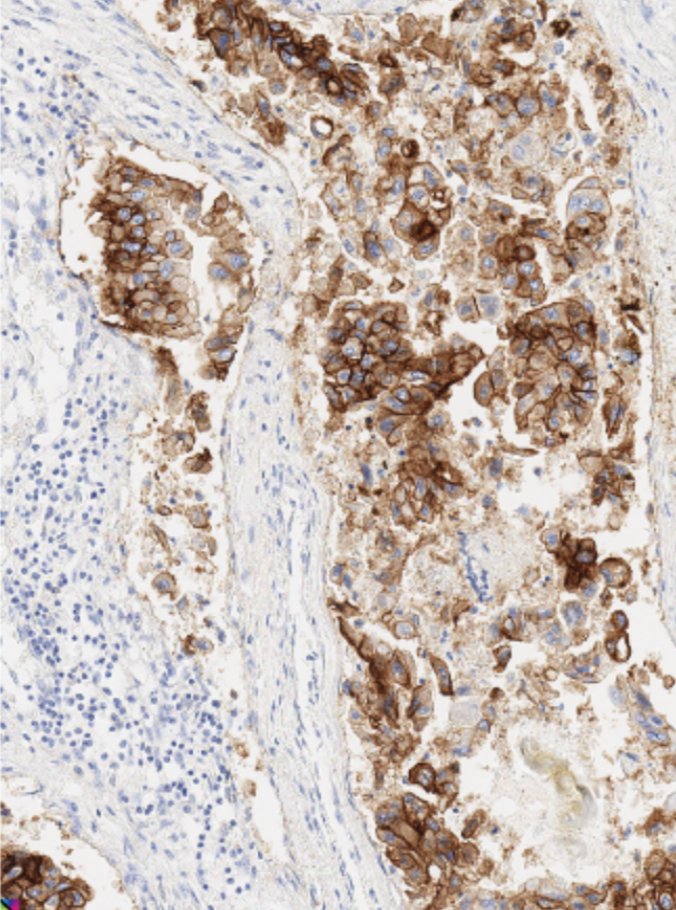
B7-H7 staining in lung
adenocarcinoma
STRATEGY
B7-H7/HHLA2 - A potential biomarker to identify patients most likely to respond
High expression of B7-H7 on tumor cells and limited expression it normal tissues makes in an important potential biomarker for selection of patients most likely to respond to therapeutics targeting the B7-H7 checkpoint axis or directly targeting B7-H7.
We are developing an immunohistochemistry assay for detection of B7-H7 that will be used to select participants in clinical studies in addition to exploring integrated biomarker strategies to define optimal patient populations for different treatment approaches.
NPX267 (A KIR3DL3 SPECIFIC ANTIBODY)
Designed to Reverse T and NK Cell Suppression
Our co-founders independently identified KIR3DL3 as the inhibitory receptor for B7-H7.
KIR3DL3 binding to B7-H7 interferes with the anti-tumor potential of T and NK cells and can contribute to tumor immune escape.
KIR3DL3 is upregulated on a subset of antigen-experienced, exhausted effector memory T cells, called TEMRA cells, and on a subpopulation of NK cells.
NPX267 is being studied in a phase 1 clinical trial in solid tumor malignancies known to express B7-H7.
NPX887 (A B7-H7/HHLA2 SPECIFIC ANTIBODY)
Designed to block immunosuppression by KIR3DL3 while sparing immunostimulation by TMIGD2
NPX887 targets B7-H7 to block its interaction with KIR3DL3 and to prevent immunosuppression of T and NK cells
NPX887 enables the interaction of B7-H7 with its other ligand, TMIGD2, which can stimulate T and NK cell activation.
NPX887 has enhanced Fc receptor function to potentiate ADCC- mediated destruction of B7-H7-positive tumor cells
NPX887 is being studied in patients with solid tumor malignancies known to express B7-H7 in a phase 1 clinical trial.
